Problem Overview
The Repeated String problem on HackerRank asks you to determine how many times the letter 'a' appears in the first n characters of an infinitely repeated string.
You are given:
- A string
sthat repeats infinitely. - An integer
nrepresenting the number of characters to consider from the infinite string.
The goal is to efficiently count the number of 'a' characters without actually constructing the infinitely repeated string. This problem is excellent for practicing mathematical reasoning combined with string manipulation.
Understanding the repeating pattern and how to scale the count to the required length is key. A naive approach of building the entire string would be inefficient for large n.
Problem Difficulty & Tags
The Repeated String problem is considered an Easy-level problem on HackerRank. It helps strengthen your understanding of string manipulation and efficient counting techniques.
- Difficulty: Easy
- Tags: Strings, Math, Greedy Algorithms, Iteration, Counting
This problem is ideal for beginners to practice combining simple arithmetic with string analysis for optimal solutions.
Understanding the Problem
In the Repeated String problem, you are given a string s that repeats infinitely, and you need to count how many times the letter 'a' appears in the first n characters of this infinite string.
Key points to understand:
- The string
srepeats infinitely: for example, ifs = "abc", the infinite string is"abcabcabc...". - You only need to consider the first
ncharacters of this infinite repetition. - The goal is to count
'a'efficiently without generating the full repeated string, especially for very largen. - Think in terms of full repetitions of the string and the remaining partial substring at the end.
The challenge tests both your ability to analyze patterns in strings and your skills in using arithmetic for efficient computation.
Approach / Logic Explanation
To solve the Repeated String problem efficiently, we focus on counting 'a' in the original string and then scaling it based on how many times the string repeats within n characters.
- First, count the number of
'a'characters in the given strings. Let’s call thiscount_a_in_s. - Calculate how many full repetitions of
sfit inton. This isn / s.size(). - Multiply
count_a_in_sby the number of full repetitions to get the total'a'count in the complete cycles. - Handle the remaining substring by taking
n % s.size()characters from the start ofsand count how many'a'characters are in this partial string. - Sum the counts from the full repetitions and the remaining substring to get the final answer.
This approach avoids creating the entire repeated string and works efficiently even for very large n, giving a solution in O(|s|) time and O(1) extra space.
Solution Code
Below is the C++ implementation for the Repeated String problem. It efficiently counts the number of 'a' characters without constructing the infinitely repeated string.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s;
long long int n;
cin >> s >> n;
long long int ans = 0;
// Count 'a' in the original string
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
if(s[i] == 'a') ans++;
}
// Multiply by number of full repetitions
ans = ans * (n / s.size());
// Count 'a' in the remaining substring
for(int i = 0; i < n % s.size(); i++) {
if(s[i] == 'a') ans++;
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
Step-by-Step Walkthrough
Let’s break down how the solution works using an example:
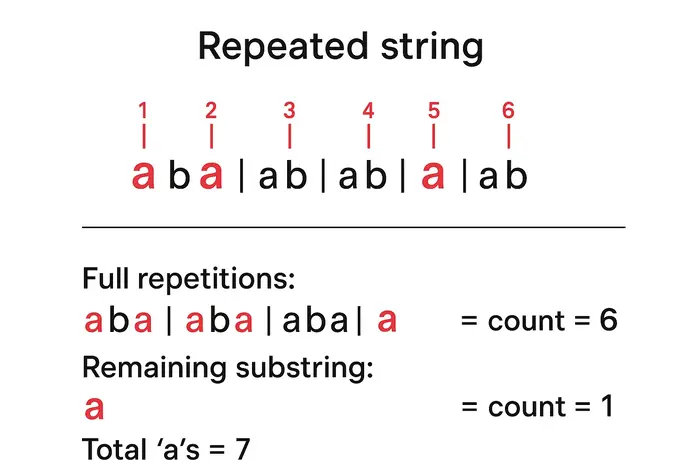
Example: s = "aba", n = 10
- Count the number of 'a' in the original string "aba":
- 'a' appears 2 times →
count_a_in_s = 2
- 'a' appears 2 times →
- Calculate how many full repetitions of "aba" fit into 10 characters:
- 10 / 3 = 3 full repetitions
- Multiply count of 'a' by 3 → 2 * 3 = 6
- Handle the remaining characters:
- 10 % 3 = 1 remaining character
- Check first 1 character of "aba": 'a' → add 1 to total
- Total 'a' count = 6 + 1 = 7
This approach ensures efficiency because we never construct the full repeated string, which is especially important for very large n.
Sample Input & Output
Here are some examples to illustrate the input and expected output:
| Input | Output | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| s = "aba" n = 10 | 7 | "aba" repeats → "abaabaabaa", 'a' appears 7 times. |
| s = "a" n = 1000000 | 1000000 | Single character 'a' repeated 1,000,000 times → count = 1,000,000. |
| s = "abcac" n = 10 | 4 | "abcac" repeats → "abcacabcac", 'a' appears 4 times. |
Time & Space Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity
The solution iterates through the original string s twice: once to count 'a' in the full string and once for the remaining substring. For a string of length m, this results in a O(m) time complexity. It does not depend on n, so even for very large n, the solution remains efficient.
Space Complexity
The solution uses only a few variables to store counts and indices. No additional arrays or data structures proportional to the input size are used, resulting in O(1) extra space.
Overall, this approach is both time and space efficient, making it suitable for extremely large input values.
Mistakes to Avoid & Tips
n, this will lead to memory issues and is inefficient.n % s.size() and count 'a' in this part.n.n, using a naive approach to loop through each character will exceed time limits. Use arithmetic to optimize.Related Problems
If you enjoyed solving Repeated String, here are some similar problems that focus on string manipulation, pattern repetition, and counting efficiently:
- String Construction – Count operations to build a string efficiently.
- Alternating Characters – Remove consecutive duplicate characters.
- Mars Exploration – Compare strings and count differences efficiently.
- Explore more String problems on HackerRank
Conclusion
The Repeated String problem is a great exercise to practice efficient string manipulation and pattern analysis. By counting the occurrences of 'a' in the original string and scaling it according to the repetitions and remaining substring, we can solve the problem without generating the full infinite string.
Key takeaways:
- Understand patterns in repeated strings to avoid unnecessary computation.
- Always handle the remaining substring after full repetitions for accurate counts.
- Use arithmetic and simple iteration instead of building huge strings to optimize performance.
- The solution runs in O(|s|) time and uses O(1) extra space, making it scalable for very large
n.
I encourage you to practice more string repetition and counting problems on HackerRank to strengthen your problem-solving skills and become comfortable with efficient algorithms.
 153 views
153 views